Japan, a country with both traditional cultural charm and modern technological strength, has long been a destination that many international students yearn for. Its high-quality educational resources, safe social environment, unique cultural experience, and broad employment opportunities after graduation all make Japan a popular choice for studying abroad. However, to realize this dream of studying abroad, a visa is undoubtedly a key link.
In the long journey of studying in Japan, a visa is like a golden key to open the treasure house of knowledge. It is not only the certificate of your legal study and life in Japan, but also an important identity certificate throughout the entire study abroad process. From the initial language school study, to the subsequent university study, and even the job exploration after graduation, every stage is closely related to the visa. Correctly understanding and managing visas can make your study abroad journey smoother and make full use of the various opportunities provided by Japan.
This article will provide you with a comprehensive analysis of the entire process of obtaining a Japanese study visa, with a special focus on the seamless transition from language school to university. We will provide a detailed introduction to the visa application and conversion process at different stages, provide you with a clear timeline, and provide practical advice and precautions. Whether you are a student planning to study in Japan or a student who has already embarked on the road to studying in Japan, this article will be your right-hand man, helping you to be confident in the key issue of visas and fully control your study abroad plans.
Overview of Japan Student Visa
There are two main types of study visas in Japan: study visas and student visas. Study visas are for students studying Japanese at language schools or other educational institutions, and are usually valid for 6 months to 1 year. Student visas are for students studying at universities, graduate schools (graduate schools) or vocational schools in Japan, and are generally valid for 1 to 4 years, depending on the course of study. It is worth noting that although the two visas have different names, they are basically the same in terms of application procedures and the rights granted.
The general process of visa application can be summarized as follows: First, the applicant needs to obtain admission permission from a Japanese educational institution. Then, the Japanese educational institution applies to the Japanese Ministry of Justice for a “Certificate of Eligibility”. Once the certificate is obtained, the applicant needs to submit a visa application at the Japanese embassy or consulate in their home country. This process usually takes 1-3 months, so it is recommended to plan ahead.
During the application process, there are several important tips that need special attention: First, make sure that all submitted documents are true and accurate. Any false information may lead to visa rejection. Secondly, financial guarantee is one of the key points of visa review. Applicants need to prove that they have sufficient financial ability to pay for study and living expenses in Japan. In addition, maintaining a good study plan and a clear study purpose are also key factors in obtaining visa approval. Finally, after the visa is approved, please carefully check the information on the visa to ensure that it is consistent with your actual situation.
Applying for a Japanese study visa may seem complicated, but as long as you are well prepared and complete each step step by step, you can successfully obtain this “ticket” to Japan. Understanding these basic information will lay a solid foundation for your study abroad journey, allowing you to fully immerse yourself in the rich and colorful learning and cultural experience the moment you set foot on Japanese soil.
Timeline chart: Japan study visa planning
Visa planning for studying in Japan can be roughly divided into four main stages, each with its own specific visa requirements and considerations. Let’s explore each stage in detail in chronological order.
Phase 1 (0-6 months): Applying to a language school. This is the starting point of your study abroad journey in Japan. At this stage, you will need to choose a suitable language school and obtain admission. You will then use this admission to apply for a student visa. This process usually takes 3-6 months. Please note that choosing a reputable language school is crucial to successfully obtaining a visa.
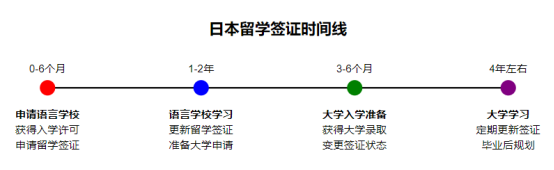
Phase 2 (1-2 years): Language school study period. After obtaining your visa, you will begin studying at a language school in Japan. This phase usually lasts 1-2 years. During this period, you will need to renew your student visa regularly, usually once a year. At the same time, this is also a critical period for you to prepare for the next stage of university applications. Remember to apply for “Permission for Activities Outside the Status of Qualification” so that you can work legally while studying.
Phase 3 (3-6 months): University admission preparation period. This is a transitional period that usually begins when language school studies are about to end. You need to prepare university application materials and take the necessary entrance exams, such as EJU (Examination for Japanese University Admission for International Students) or individual entrance exams for each university. Once you receive a university acceptance letter, you will need to apply to change your visa status from language school student status to university student status. This process takes 3-6 months.
Phase 4 (about 4 years): University study period. This is the main phase of your study abroad career, usually lasting 4 years (undergraduate). During this phase, you will need to renew your student visa regularly, usually every year or every two years. During college, you may consider participating in internships or continuing to work, remember to make sure these activities comply with your visa regulations. As you approach graduation, you will need to start thinking about your post-graduation plans, which may include further study, employment in Japan, or returning to your home country.
Visa application for language school
Choosing a language school is the first step to study in Japan and the key to applying for a visa. When choosing a language school, you need to consider factors such as the school’s recognition, curriculum, location, and tuition fees. In particular, it should be noted that only Japanese language education institutions approved by the Japanese Ministry of Justice can issue a Certificate of Eligibility for international students, which is a necessary condition for applying for a visa. It is recommended to choose a school registered with the Japanese Language Education Promotion Association (NISSHINKYO), which is usually more trusted by the Japanese Immigration Bureau and is conducive to obtaining a visa smoothly.
The steps to apply for a language school visa usually include: first, submit an application to the language school of your choice and obtain admission; second, the school will apply for a Certificate of Eligibility from the Immigration Bureau of Japan on your behalf; after obtaining the certificate, the applicant needs to prepare relevant materials and submit a visa application to the Japanese Embassy or Consulate in China. The whole process usually takes 3-6 months, so it is recommended to start preparing one year in advance. It is worth noting that some language schools may require applicants to pass the Japanese Language Proficiency Test (JLPT) N5 level first, and this requirement varies from school to school.
The list of materials required to apply for a language school visa includes: passport, certificate of eligibility, admission permit, final academic certificate (graduation certificate), Japanese language learning certificate, proof of financial ability (bank deposit certificate or sponsor’s income certificate), ID card copy, household registration copy, photo, etc. If sponsored by parents or relatives, proof of sponsorship and proof of kinship are also required. All Chinese materials need to be translated into Japanese and stamped by the translation company.
During the application process, applicants may encounter some common problems. For example, many people worry that their Japanese level is not good enough. In fact, most language schools do not require applicants to have a Japanese foundation, but if you have some Japanese learning experience, it will increase the chances of successful application. Another common problem is proof of funds, which usually requires a deposit amount that can cover at least one year’s tuition and living expenses. If personal deposits are insufficient, parents or relatives can serve as financial guarantors. In addition, some applicants worry whether their older age will affect their application. In fact, as long as you can prove that your study purpose is clear and you have sufficient financial ability, age is not a decisive factor.
Finally, it is worth mentioning that it is important to be patient and careful during the application process. Carefully checking each document to ensure that the information is accurate will greatly increase the possibility of visa approval. At the same time, it is recommended to pay close attention to the latest policies of the Japanese Immigration Bureau, as visa policies may be adjusted at any time. If you encounter difficulties in the application process, you can seek help from professional study abroad agencies, who can provide more professional and personalized guidance.
Through the above detailed introduction, I believe that readers can have a comprehensive understanding of the visa application at the language school stage. This is not only the first step to study in Japan, but also an important bridge to Japan’s higher education. As long as you are fully prepared, I believe that every student who dreams of studying in Japan can successfully obtain a visa and start their journey to study in Japan.
Visa maintenance during language school
It is extremely important to properly maintain your student visa status while studying at a language school in Japan. This is not only related to your legal residence, but also directly affects your future study and work opportunities. This section will detail key aspects such as visa extension applications, part-time work permits, and study requirements.
1. Visa extension application
Most language schools offer a study period of 1-2 years, while the initial study visa is usually only valid for 1 year. Therefore, many students need to apply for a visa extension in Japan. The application time is usually within 3 months before the expiration of the existing visa. The materials you need to prepare include: proof of enrollment, transcripts, attendance records, bank deposit certificates, etc. It is worth noting that the Japanese Immigration Bureau will strictly review your academic performance and financial ability. If your attendance rate is too low or your financial situation is unstable, it may affect your extension application. It is recommended that you prepare all materials 1-2 weeks in advance and submit the application at least 1 month before the visa expires to ensure sufficient processing time.
2. Part-time work permission (permission to engage in activities other than those permitted by the status of employment)
Many international students would like to supplement their living expenses by working part-time. However, a student visa does not include the right to work. You need to apply for “Permit for Activities Outside the Status of Residence” to work legally. This permission usually allows you to work no more than 28 hours per week (extended to 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week during long vacations). The application process is relatively simple: you can apply directly at the airport when you enter Japan, or go to the local immigration bureau later. It is important to note that some industries (such as the sex industry) are explicitly prohibited for international students. Illegal work may result in the revocation of your visa or even forced deportation. Therefore, be careful when choosing a part-time job to ensure that it complies with the regulations.
3. Learning progress requirements and attendance rate
Maintaining a good learning progress and high attendance rate is not only a requirement of the language school, but also a key factor in maintaining the validity of your visa. The Immigration Bureau of Japan has strict supervision over the learning status of international students. Generally, language schools require students to maintain an attendance rate of more than 90%. If you miss classes for more than one week in a row, the school is obliged to report to the Immigration Bureau. Low attendance rate will not only affect your visa extension application, but in serious cases may lead to the cancellation of your visa. In addition, your learning progress will also be closely monitored. If your Japanese language ability does not improve significantly within the specified time, it may also affect your visa status. Therefore, it is recommended that you take every class seriously, actively participate in learning activities, and regularly evaluate your language progress.
In general, maintaining your visa status during your language school years requires vigilance and motivation on many fronts. Renewing your visa on time, working legally, and maintaining high attendance and good grades are all important factors in ensuring that you successfully complete your language studies and pave the way for future university life or work. Remember, every action you take may affect the quality of your studies and life in Japan, so always be responsible and plan.
Transition from language school to university
The transition from language school to Japanese university is a critical stage in your study abroad experience. This process requires not only academic preparation but also involves complex administrative procedures. This section will outline the main aspects of this transition period to help you make the transition to a smooth educational stage.
Preparing for university applications is a process that requires long-term planning. First, you need to research and choose the right university and major, considering factors such as school type, reputation, major ranking, and location. It is crucial to understand the application requirements of the target university, and usually you need to prepare materials such as admission application forms, academic qualifications, and language proficiency certificates. It is recommended to start preparing at least one year in advance and pay close attention to the application deadline.
Japanese language proficiency is a key requirement for admission to Japanese universities. Most universities require a Japanese language level of N2 or N1, which can be demonstrated through the Japanese Language Proficiency Test (JLPT). While studying at a language school, you should make the JLPT exam an important goal, develop a reasonable study plan, and strive to obtain the required level certificate before applying.
Changing your visa status is an important part of the transition period. After being admitted to a university, you need to apply for a visa change from a language school student to a university student. This process includes preparing the necessary documents, filling out the application form, and submitting the application to the Immigration Bureau. It is recommended to consult the school or professional organization in advance to ensure that this process is completed smoothly.
During the transition period, you need to pay attention to several key issues: manage your time properly, make good financial plans, arrange accommodation, maintain valid residence status, and adapt to the new learning environment. You can also use language school resources and keep in touch with seniors to gain valuable experience and advice.
With careful planning and careful preparation, you can successfully complete the transition from language school to university and lay a solid foundation for university life in Japan. When you encounter questions, please seek help from relevant institutions in a timely manner. I wish you a smooth start to your new learning journey!
Visa Management at the University Level
Studying at a Japanese university is an important goal for many international students. Compared with the language school stage, visa management at the university stage has its own unique features, which require students to pay special attention to. This section will introduce in detail the characteristics of university study visas, the renewal and extension process, the relationship between academic requirements and visas, and internship and part-time regulations.
1. Characteristics of university study visa
A Japanese university student visa, often referred to as a “study abroad” visa, is valid for up to 4 years and 3 months, which matches the standard duration of most undergraduate programs. Compared to a language school visa, a university visa gives students more flexibility and opportunities. Students holding this type of visa can arrange their study schedule more freely, participate in on-campus and off-campus activities, and even have the opportunity to apply for a longer part-time work permit.
2. Visa renewal and extension
Although the initial university study visa is valid for a longer period, students still need to pay attention to regular renewal. Usually, the first visa is valid for 1 year and 3 months or 2 years and 3 months. Subsequent renewals may be granted for longer periods, but this depends on the student’s academic performance and the school’s recommendation. Visa renewal should be carried out within 3 months before expiration. The materials required include: proof of enrollment, transcripts, attendance records, financial proof, etc. Students are advised to collect the required documents in advance to avoid affecting their study plans due to incomplete materials.
3. The relationship between academic requirements and visas
In Japan, academic performance is closely related to visa renewal. The Immigration Bureau of Japan attaches great importance to the learning attitude and results of international students. Students need to maintain a good attendance rate (usually more than 80% is required) and obtain credits consistent with the academic year. If students frequently miss classes or have poor academic performance, it may affect the renewal of their visa. In serious cases, it may even lead to the cancellation of the visa. Therefore, maintaining a positive learning attitude is not only related to academic achievement, but also directly affects the legal residence rights in Japan.
4. Internship and part-time employment regulations
The Japanese government understands that international students may need to work part-time to cover some of their study and living expenses. Students holding a university student visa can work part-time without affecting their studies after obtaining “permission for activities other than those permitted by the status”. Generally, working hours per week should not exceed 28 hours (extended to 8 hours per day during long vacations such as summer vacation). It is worth noting that certain industries such as the sex industry are expressly prohibited. Course-related internships are usually not counted towards this 28-hour limit, but permission must still be obtained from the Immigration Bureau.
Complying with these regulations is not only a legal requirement, but also an important way to ensure that students can balance study and work. Proper management of the university visa will not only allow international students to focus on their studies, but also lay a good foundation for further study or employment in Japan in the future.
Post-graduation options and visa changes
After graduating from a Japanese university, international students face important life decisions. Whether continuing their studies, looking for a job, or staying in Japan temporarily to look for opportunities, they will need appropriate visa support. This section will detail three common visa change options after graduation to help you plan for the future.
1. Visa changes for further studies
If you decide to continue your studies in Japan, such as upgrading from an undergraduate to a master’s degree or from a master’s to a doctoral degree, you will need to apply to change your visa type. Although you already have a student visa, you still need to renew it. First, you need to obtain admission permission from your new school. After that, go to the nearest immigration bureau and submit an “application for permission to change your status of residence.” The required materials usually include: admission permission from the new school, graduation certificate from the current school, new certificate of eligibility, etc. This process is usually simpler than applying for a student visa for the first time, but it is recommended to start preparing at least 1-3 months before the expiration of your current visa.
2. Employment visa conversion
Many international students choose to work in Japan, which requires converting their student visa to a work visa. First, you need to find a company willing to hire you and get a job offer. Depending on the nature of your job, you can apply for a status of residence such as “Technology, Humanities, International Business” or “Skills”. Application materials usually include: Application for Change of Status of Residence, Employment Contract, Company Profile, Final Education Certificate, etc. It is worth noting that the content of your job must be related to your major. For example, engineering graduates can work in IT or engineering, while liberal arts graduates can work in translation, marketing, etc. This process may take 1-3 months, so it is recommended to start preparing before graduation.
3. Specified Activities Visa (Job Hunting Activities)
If you have not found a job when you graduate, but want to stay in Japan to continue looking for opportunities, you can apply for a “Specified Activities (Continued Employment Activities)” visa, commonly known as a “job-seeking visa.” This visa allows you to stay in Japan for up to 6 months after graduation (extendable once, up to 1 year in total) specifically for job hunting. Application materials include: application for change of status of residence, graduation certificate, transcript, specific job-seeking activity plan, etc. The advantage of this visa is that it gives you plenty of time to find an ideal job in Japan without having to rush to accept an offer that you are not satisfied with. But please note that you need to actively participate in job hunting activities during this period and keep relevant certificates.
No matter which path you choose, remember that planning ahead and preparing sufficient materials are the key to successfully completing the visa change. At the same time, pay close attention to the latest policy changes of the Japanese Immigration Bureau, as visa regulations may be fine-tuned. If you are unsure about the process, it is recommended to consult the school’s international student office or a professional administrative scrivener, who can provide the most professional advice.
In short, the Japanese government welcomes outstanding international students to stay in Japan for further study or work. As long as you make full use of the knowledge and experience you have accumulated during your study in Japan, I believe you will definitely find a development path that suits you. Whether you choose to continue studying, go directly to work, or find a job first and then decide, you must bravely follow your goals and believe that a bright future is waiting for you.
Practical suggestions and precautions
Many students often encounter some misunderstandings and challenges during the application process for a Japanese study visa. This section will provide you with some practical advice to help you avoid common pitfalls, increase your visa approval rate, and properly manage important documents.
Common Misunderstandings When Applying for a Visa
One of the most common misconceptions is underestimating the time required for a visa application. Many students believe that a visa application is a quick process, when in reality it can take weeks or even months. Therefore, it is recommended that you start preparing your visa application materials at least 3-6 months before your intended date of enrollment.
Another misconception is to ignore the importance of proof of funds. The Immigration Bureau of Japan attaches great importance to the applicant’s financial ability. Some students may think that as long as they have a certain amount of savings, it is enough, but in fact, the legality and stability of the source of funds are equally important. Make sure that your proof of funds is not only sufficient in amount, but also clearly shows the source and stability of the funds.
In addition, some applicants may try to conceal or embellish their background information, such as education or work experience. This is an extremely dangerous practice. Once false information is discovered, it will not only lead to the rejection of this visa application, but may also affect future applications. Honesty and transparency are the basic principles of visa applications.
1. Tips to improve visa approval rate
To improve your visa approval rate, you must first ensure the completeness and accuracy of all application materials. Read the application guide carefully, prepare a checklist, and check each document item by item. Pay special attention to the validity period of the materials and ensure that all documents are up to date when submitted.
Secondly, it is crucial to provide a detailed and coherent study plan. Your study plan should clearly demonstrate why you choose to study in Japan and how this experience will help you achieve your long-term goals. Make sure your study plan is consistent with your academic background and career plans.
Also, if you have the opportunity, consider taking the Japanese Language Proficiency Test (JLPT). Even if the program you are applying for is taught in English, demonstrating your passion and ability to learn Japanese will add points to your application. This shows that you have the willingness and ability to integrate into Japanese society.
Finally, if your application involves special circumstances, such as a long gap between academic qualifications or a previous visa rejection, it is recommended that you proactively provide a detailed explanation. Frankly explaining these circumstances and providing relevant supporting documents can increase the visa officer’s understanding and trust in your application.
2. Storage and use of important documents
Throughout the study abroad process, it is crucial to properly keep and use important documents. First, it is recommended that you make multiple copies of all important documents and scan them electronically. Keep the originals, copies, and electronic versions separate to prevent loss or damage.
Your passport is one of the most important documents you have. It is recommended that you carry a copy of your passport with you while in Japan, but keep the original in a safe place. Also, pay close attention to the expiration date of your passport to ensure that it remains valid throughout your study abroad period.
In Japan, the Residence Card is also an extremely important document. It is not only proof of your legal residence, but is also often used for identity verification. Please always carry your Residence Card with you, but also keep a copy and electronic scan of it.
For other important documents, such as admission permits, transcripts, and diplomas, it is recommended that you keep the originals in a safe place and prepare notarized copies in case of emergency. Check the validity and status of these documents regularly to ensure that they can be used in time when needed.
Finally, it is recommended that you create a digital folder to store electronic copies of all important documents. You can upload these files to a cloud storage service so that you can always access this important information even if the originals are lost. But remember to pay attention to information security when using cloud services, choose a reliable service provider and use strong password protection.
By avoiding these common pitfalls, adopting tips to improve your chances of success, and properly managing important documents, you will greatly increase your chances of successfully obtaining a Japanese student visa and lay a solid foundation for your study abroad journey.
Conclusion
In this article, we explore the entire process of obtaining a Japanese study visa, from language school to university. Although this journey is full of challenges, each step can be smooth sailing as long as you are well prepared. Let’s briefly review the key points of the entire process.
First of all, the preparation for visa application should not be underestimated. From choosing a suitable language school to preparing detailed application materials, every step needs to be taken seriously. In particular, the preparation of core documents such as proof of funds and study plan must be rigorous and meticulous. During the language school stage, in addition to studying Japanese hard, you must also pay attention to visa extension and maintenance to lay the foundation for future studies.
The transition to university is an important turning point in the study abroad career. This stage requires not only focusing on the preparation for the university entrance examination, but also timely handling of visa status changes. After entering university, visa management is still a long-term task that requires regular updates and strict compliance with relevant regulations. At the same time, you must also plan ahead and make plans for your development after graduation.
The most important thing during the entire study visa process is to remain honest and law-abiding. Whether it is application or daily life in Japan, you must always abide by relevant laws and regulations. At the same time, properly keeping important documents and establishing good document management habits will save you a lot of unnecessary trouble during the entire study abroad period.
For those of you who are about to embark on the journey of studying in Japan, I want to say that this process may be full of challenges, but it is also full of opportunities and the possibility of growth. Reasonable planning is the key to success. Make a detailed timetable and organically combine various links such as visa application, language learning, and school application, which will greatly increase your chances of success.
Remember, studying abroad is not just about getting a diploma, it is also a rare opportunity for cultural experience and personal growth. While focusing on your studies, you should also actively integrate into Japanese society and experience the unique charm of Japanese culture. These experiences will become a valuable asset in your life.
Finally, I sincerely hope that every reader can successfully obtain a Japanese study visa and realize their dream of studying abroad. I believe that through your efforts and persistence, you will be able to gain rich knowledge, experience and good memories in your study life in Japan. I wish you academic success and a bright future!
Life is a journey, and studying abroad is one of the most exciting chapters in this journey. Set off with courage and determination, and believe that a bright future is beckoning you!








